Alopecia or hair loss in men is such a stressful disease that any man having this disease tries to get the treatment as soon as possible. Alopecia affects the lifestyle of the patient to a much higher extent. Under the effect of this disease, hair is lost from some or all areas of the body, usually from the scalp due to the body’s failure to recognize its own body cells and subsequent destruction of its own tissue. It results in bald spots on the scalp, especially in the first stages and then spreads to the whole body.
The hair tends to fall out over a short period of time, with the loss commonly 2occurring more on one side of the scalp than the other. Hair will also tend to pull out more easily along the edge of the patch where the follicles are already being attacked by the body’s immune system than away from the patch where they are still healthy.
Alopecia tends to occur most often in adults of 30 to 60 years of age. However, it can also affect older individuals and rarely, young children. For most patients, the condition resolves without treatment within a year, but hair loss is sometimes permanent. A number of treatments are known to aid in hair re-growth. Most of them involve the use of medications. It is said that the use of medications causes other complications in the affecting individuals.
HOW COULD ALOPECIA INHIBIT THE FUNCTION OF TESTOSTERONES?
It has been observed from scientific studies that the use of certain medications for the treatment of alopecia is the reason behind inability of testosterones (male hormones) to function properly.
This is due to the target of alopecia-treating medicines i.e. 5-α-reductase enzyme. Alopecia treating medications inhibit this enzyme to carry out its activity to convert testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) because it has been postulated that hair follicles are sensitive to DHT. In alopecia affecting men, the levels of DHT have shown to be very high. Scientists have seen that DHT shrinks hair follicles, and that when DHT is suppressed, hair follicles continue to thrive.
DHT is the more potent form of testosterone inside body, which is essential for sexual activities in men. Once 5-α-reductase enzyme is inhibited, then, DHT will also not be produced by the body and its ultimate function of sexual activities will also be inhibited. This condition gives rise to the development of more complications such as erectile dysfunction in men, which affects their overall well-being.
Alopecia
- The diagnosis of alopecia can be usually established based on clinical presentation in men.
- Trichoscopy can be used for further evaluation.
- Biopsy may be needed to exclude other causes of hair loss
- Histologywould demonstrate perifollicular fibrosis
- Alopecia-generated testosterone inhibition in men
- Erectile dysfunction
- Diminished sexual activities
- Loss of libido
- Depression
- Loss of muscle mass and strength
TREATMENT
For alopecia – instead of inhibiting 5-α-reductase enzyme
Other treatment options that don’t involve testosterone or DHT include:
- Minoxidil: 5% topical minoxidil solution is applied once or twice a day to help stimulate hair on the scalp. This treatment has great benefit because if a person’s hair grows back completely with topical minoxidil, treatment can be stopped. This medication is also considered easy to use.
- Ketoconazole: Ketoconazole is helpful in countering the effects of dihydrotestosterone in people who have alopecia. It should be usedat the dosage prescribed by your doctor.
- Laser Treatment
- Surgical Hair Follicle Transplant
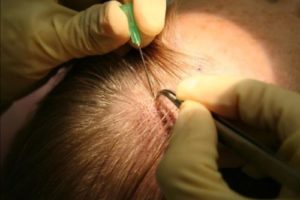
- Intralesional corticosteroid injections: Use of corticosteroids that are injected into bare patches of skin with a tiny needle. These injections are repeated about every 4-6 weeks and are usually given by a dermatologist.
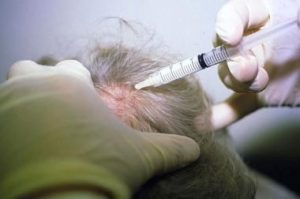
- For alopecia-generated testosterone complication
If this complication occurs with alopecia, then, its treatment strategies involve the following, which can be implemented after discussion with doctor treating your alopecia:
- Ginseng herb: This natural remedy can increase libido, enhance sports performance, boost weight loss, stimulate the production of androgen hormone, and ease depression, high blood pressure and fatigue.
- Tribulus terrestris: It has ability to increase testosterone levels. The plant’s fruit, leaf, and root can be crushed to be used in tea.
- Yohimbe: Also known as yohimbine, this herb may benefit people with low T and symptoms of low T.
- L-argininge: L-arginine doesn’t boost a person’s level of testosterone directly. Instead it may help treat symptoms of low T, such as ED.
- Fenugreek: This herb helps to raise testosterone levels in the body. It is also clinically proven in the form of Furosap to treat testosterone deficient men. It is able to manage testosterone deficiency, muscle mass and bone health too.













